
What happens during the formation of Okazaki fragments quizlet? … During the process of DNA replication, DNA and RNA primers are removed from the lagging strand of DNA to allow Okazaki fragments to bind to. Newly synthesized DNA, otherwise known as Okazaki fragments, are bound by DNA ligase, which forms a new strand of DNA. What happens during the formation of Okazaki fragments? … DNA polymerase catalyzes the addition of nucleotides to a growing DNA chain. Okazaki fragments are short sequences synthesized in the lagging strand because DNA polymerase can synthesize only from 5′ to 3′, and the DNA strands are antiparallel. How are Okazaki fragments synthesized quizlet? It only replicates continuously (like the leading strand), and uses DNA primers. PCR doesn’t have a leading and lagging strand, nor does it use RNA primers, okazaki fragments, etc. Okazaki fragments are formed on the lagging strand for the synthesis of DNA in a 5′ to 3′ direction towards the replication fork. Okazaki fragments are formed on lagging strands, initiated by the creation of a new RNA primer by the primosome.

DNA polymerases cannot initiate synthesis of a new DNA strand they can only add bases to an existing strand. DNA ligase joins adjacent Okazaki fragments together into a complete strand. The DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously is called the leading strand.
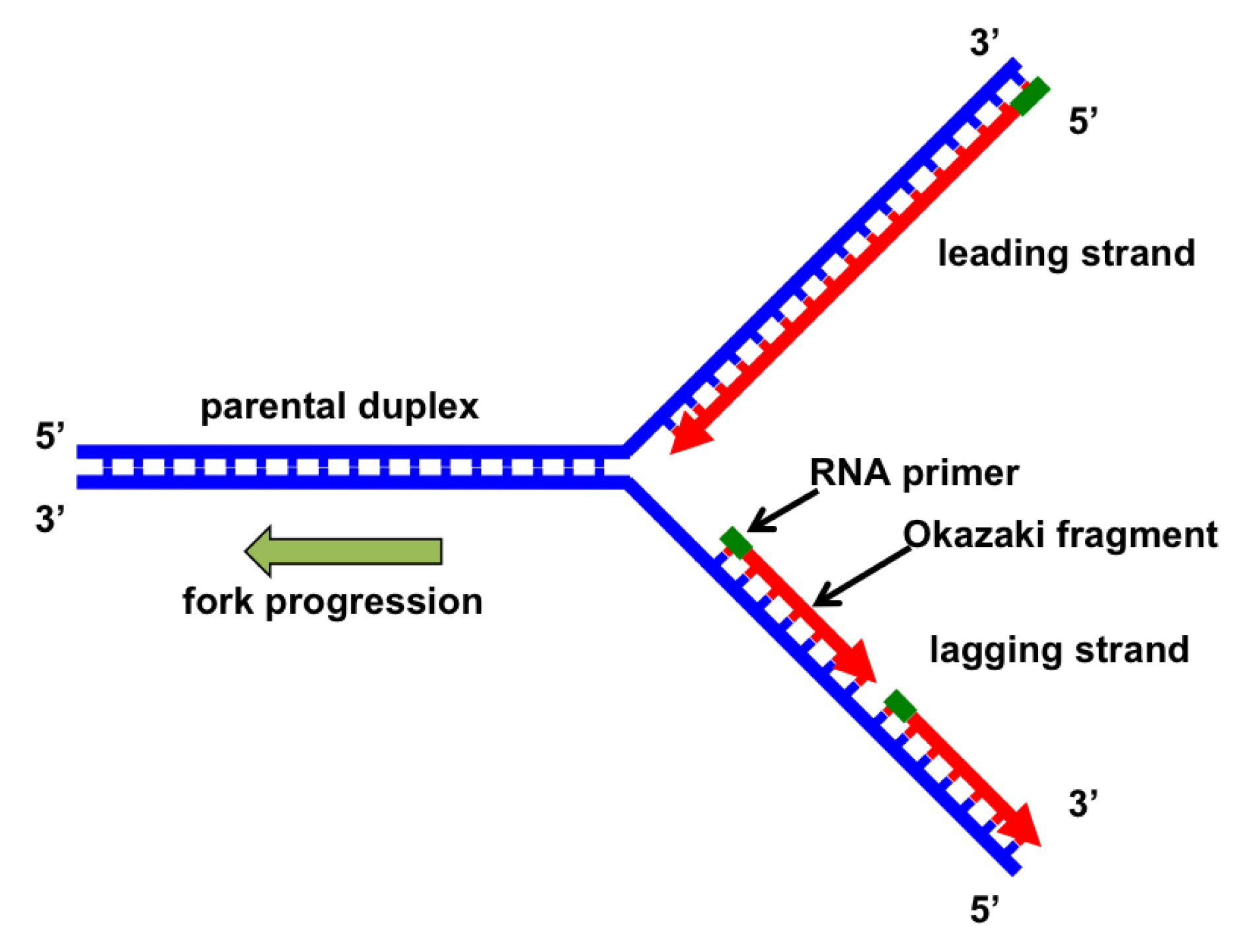
The DNA strand that is synthesized continuously is called the lagging strand. Each Okazaki fragment has its own primer. The DNA strand that grows toward the replication fork is synthesized discontinuously in short pieces called Okazaki fragments. The DNA strand that grows away from the replication fork is synthesized continuously from one initial primer. Because the 2 strands of a DNA molecule run in opposite directions, and because DNA polymerases can synthesize new strands only in the 5' to 3' direction, polymerases on opposite strands must synthesize DNA in opposite directions. DNA polymerases can add new DNA nucleotides only to the 5' end of an existing strand. Because the 2 strands of a DNA molecule run in opposite directions, they are said to be bidirectional.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
