
In patients presenting with atrial flutter after LA ablation, entrainment mapping should be performed at the CTI even if the ECG is uncharacteristic of CTI-dependent flutter. LA activation contributed little to the genesis of the flutter waves in these patients because of a significant reduction in bipolar LA voltage (0.44+/-0.20 versus 1.54+/-0.19 mV in patients with biphasic/negative flutter waves P<0.001).ĬTI-dependent flutter that occurs after LA ablation of atrial fibrillation often has atypical ECG characteristics because of altered LA activation. The CTI line was performed during the same procedure, on top of.
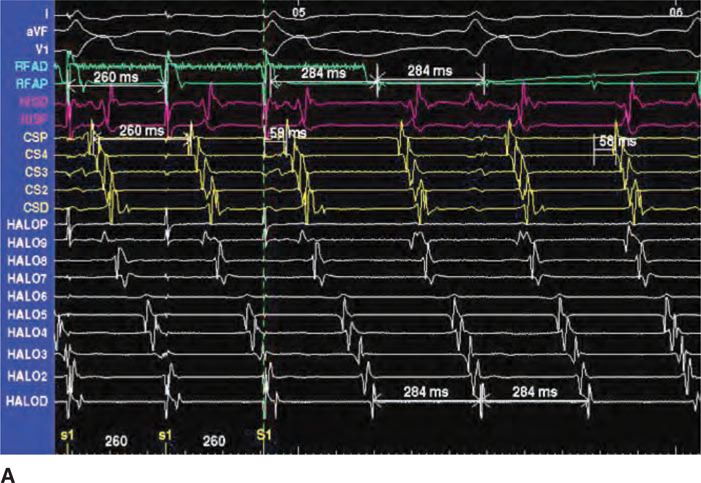
48 Figure 7 shows an example of ectopies originating from the right superior pulmonary vein, and inducing a CTI-dependent CCW AFL.
#Cti ablation flutter free#
The upright flutter waves in the inferior leads in patients with counterclockwise flutter corresponded to craniocaudal activation of the right atrial free wall. For AF ablation procedures, the CTI ablation is recommended only if the patient had a history of CTI-dependent AFL, or if induced during the procedure.

The flutter waves in the inferior leads were upright in 9 of the 15 patients (60%) with prior LA ablation and in none of the control subjects (P<0.001). The ablation procedures main target is to achieve bidirectional block through the cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI). Among the patients with prior LA ablation, mapping revealed counterclockwise activation around the tricuspid annulus in 12 of 15 patients (80%) and clockwise activation in 3 of 15 patients (20%). Thirty age- and gender-matched patients who underwent ablation of CTI-dependent flutter without prior LA ablation served as control subjects. The ECG, biatrial activation patterns, and LA voltage maps during flutter were analyzed. The effects of left atrial (LA) ablation on the characteristics of CTI-dependent flutter have not been described.įifteen patients underwent ablation of CTI-dependent flutter late after LA ablation of AF. of Internal Medicine (내과학교실) > 1.Patients who have previously undergone ablation of atrial fibrillation may experience cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI)-dependent atrial flutter during follow-up. Conclusions: In this large and long-term follow-up study, prophylactic CTI ablation had no benefit in patients with paroxysmal AF without typical AFL. This is despite a significant number of patients developing new onset atrial fibrillation. The recurrence rate of typical AFL also was not different (0.5%in PVI vs. cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI) ablation for typical atrial flutter. The recurrence rate of any AFL was not significantly different in the 2 groups (3.3% in PVI vs. The recurrence rate of AF or AFL was not different in the 2 groups (25.7% in PVI vs. All patients were followed up for at least 18 months, and the median follow-up was 3.4 years. 7 Electronic searches were conducted in EMBASE and MEDLINE from 1990 to 2007. 174.2 +/- 76.5 minutes in PVI+CTI, p=0.75). A 2006 meta-analysis reviewed the clinical efficacy and safety of AAD and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of AF. Results: There was no significant difference in procedure time between the two groups because most CTI blocks were performed during the waiting time after the PVI (176.8 +/- 72.6 minutes in PVI vs. We randomly assigned 366 patients to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) only and prophylactic CTI ablation (PVI vs.

Methods: Patients who underwent catheter ablation for paroxysmal AF were enrolled, and patients who had previous or induced atrial flutter (AFL) were excluded. However, the previous study was too small and short-term to clarify the efficacy of this block. Authors Kim, Sung-Hwan Oh, Yong-Seog Choi, Young Hwang, Youmi Kim, Ju-Youn Kim, Tae-Seok Kim, Ji-Hoon Jang, Sung-Won Lee, Man Young Joung, Boyoung Choi, Kee-Joon Citation KOREAN CIRCULATION JOURNAL, Vol.51(1) : 58-64, 2021-01 Journal Title KOREAN CIRCULATION JOURNAL ISSN 1738-5520 Issue Date 2021-01 Keywords Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter Catheter ablation Abstract Background and Objectives: Cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI) block is easily achieved, and prophylactic ablation can be performed during atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
